Transform Your Data into a Strategic Asset:
Comprehensive Data Management Solutions
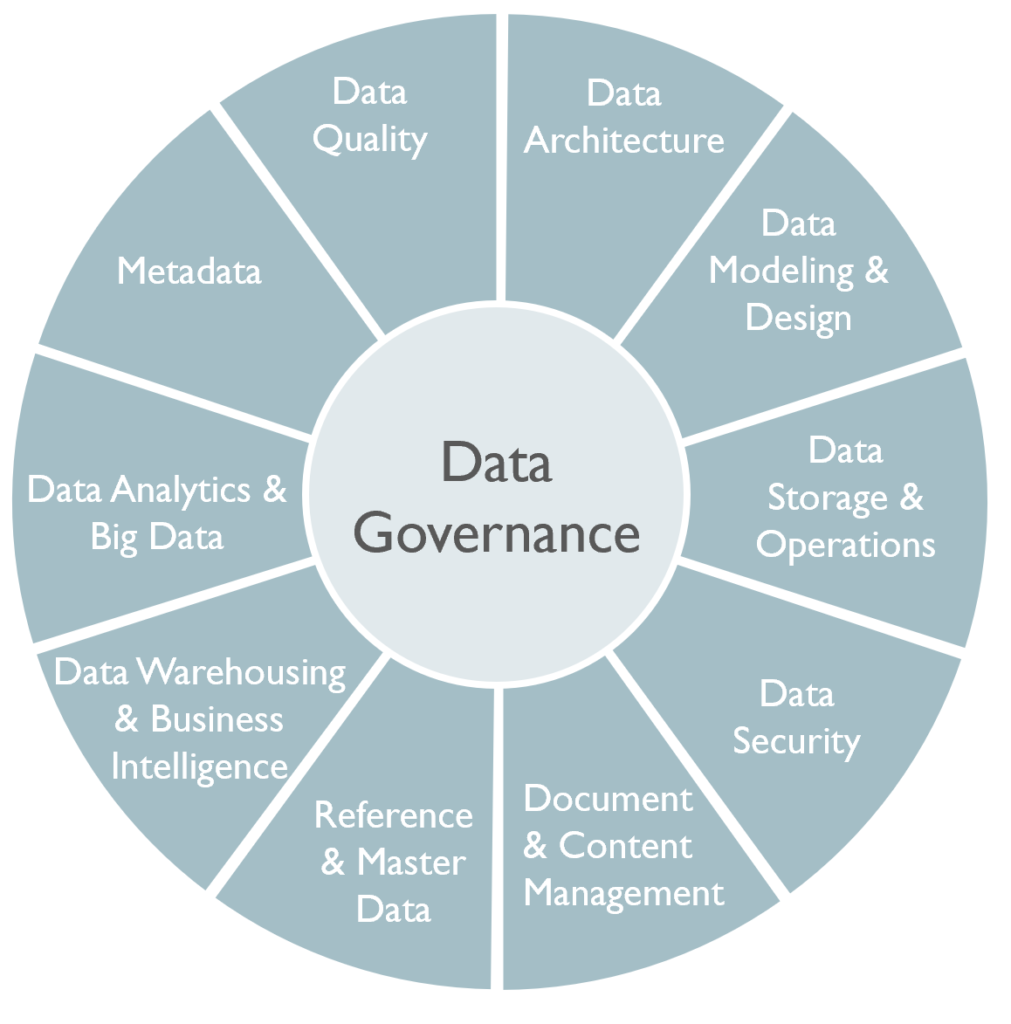
What is Data Management?
Data management is the holistic discipline of treating data as a vital resource. It encompasses the strategies, policies, and practices needed to ensure data is accurate, consistent, secure, and accessible throughout its lifecycle. It’s a continuous journey of improvement, not a one-time fix.
Why Invest in Data Management?
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting mandates like BCBS 239 and GDPR to avoid significant penalties.
- Operational Efficiency: Eliminating data silos, automating reporting, and reducing costly errors.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Enabling accurate analysis and insights for informed business decisions.
- Risk Mitigation: Protecting your organization from data breaches and financial losses.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Ensuring accurate and reliable customer data for better service.
Common Data Challenges
- Defining “critical” data. Various events led to a new local regulation (FINMA-RS 23/1) for Swiss banks as of Jan 1, 2024:
- Prevent Lehman-style collapses via stronger operational controls
- Mitigate Cyber risks after high-profile attacks on banks
- Regulate cloud/outsourcing-related risks
- Align with global standards (BCBS 239, DORA, Basel III)
- Address Swiss-specific failures (Archegos, Greensill)
- A report in a government agency showed people above age 120 still being recorded as alive. Yet, they did not receive Social Security payments. Knowledge of source of truth, where data is consumed, and system of record, where data is created as well as the lineage between them will help create correct reports.
- Risk reporting was an issue in many financial institutions during the financial crisis that began in 2007. Banks were unable to manage their risks properly because of weak risk data aggregation capabilities and risk reporting practices. This prompted the creation of a guideline (BCBS 239) that made Data Management practise mandatory for systemically relevant banks as of 2016.
- Regulatory reporting in an institution was found to be incorrect after many years of submitting data. The root causes were lack of governance, inadequate quality control and existing data quality issues.
- Automating ad-hoc reports puts data at the users’ fingertips. Lack of data quality will quickly undermine any trust in the data while the ease of use of the tools involved will determine user adoption rate.
- Redundant information in multiple appplications caused endless discussions and puzzlement about the true source of reliable data. Extensive rework and frequent reconciliations introduced unnecessary cost to the organisation.
- Data Protection laws (e.g. European GDPR) are on the rise globally and require companies to take special care of personal data. Where such laws are in place, the safeguarding of data is no longer just an internal matter, but needs to answer to the data subjects and to the regulator. Data breaches can be fined at up to 4% of a group’s annual global revenue.
- Mandatory fields in applications caused users to enter dummy information as the data entry process was not been designed with reality in mind. This is one of the root causes for data quality issues. The same applies to data that is important but the corresponding field is not flagged as mandatory and may remain empty.
- A wrong data model around customer data has required an organisation to update data redundantly and to spend considerable time in reconciling conflicting information over many years. Understanding data models will help to avoid such issues in future developments.
- US Witholding Tax brackets were not assigned correctly to safekeeping accounts, leading to real $$ losses for a large custodian.
Understanding Data Quality Dimensions:
- Accuracy: data correctly represents reality and matches with agreed source
- Completeness: all required records in the data set are present
- Consistency: the data format is consistent in the same field across all records.
- Integrity: no orphaned data due to full set of reference keys
- Resonability: when patterns meet expectation, based on common-sense judging
- Timeliness: most recent data is available
- Uniqueness: some entities may not exist more than once within the data set
- Validity: data conforms with defined set of valid values
Any of the following root causes can lead to data quality issues: lack of training, human errors, bad data entry interfaces, inconsistent business process execution, lack of ownership, incorrect assumption about data source, stale business rules and changed data structure. This enumeration is by no means complete!
What is the cost of poor data quality?
Besides internal rework to rectify data, there can be a direct bottom-line impact to the business:
- Inability to invoice correctly.
- Increased customer service calls and decreased ability to resolve them.
- Revenue loss due to missed business opportunities.
- Delay and complications in mergers and acquisitions.
- Heightened exposure to fraud and financial risks.
- Losses due to bad business decisions driven by bad data.
- Loss of business due to lack of good credit standing.
Let’s Begin Your Data Management Journey:
I provide expert guidance and practical solutions to help you unlock the full potential of your data.
My Certificates
![]() Data Science Professional | IBM | 2025
Data Science Professional | IBM | 2025
Further reading
 DAMA Guide to the Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA-DMBOK)
DAMA Guide to the Data Management Body of Knowledge (DAMA-DMBOK)
Edition 2, 2017
Authors: DAMA International